- Home›
- Amazon Web Services Support›
- Amazon Trusted Advisor
Amazon Trusted Advisor Best Practices (Checks)
Amazon Trusted Advisor
Amazon Trusted Advisor provides best practices (or checks) in four categories: cost optimization, security, fault tolerance, and performance improvement. The status of the check is shown by using color coding on the dashboard page:
Red: action recommended
Yellow: investigation recommended
Green: no problem detected
For each check, you can review a detailed description of the recommended best practice, a set of alert criteria, guidelines for action, and a list of useful resources on the topic.
Two Trusted Advisor checks are available to all Amazon Web Services customers to help improve security and performance: Service Limits, and Security Groups - Specific Ports Unrestricted.
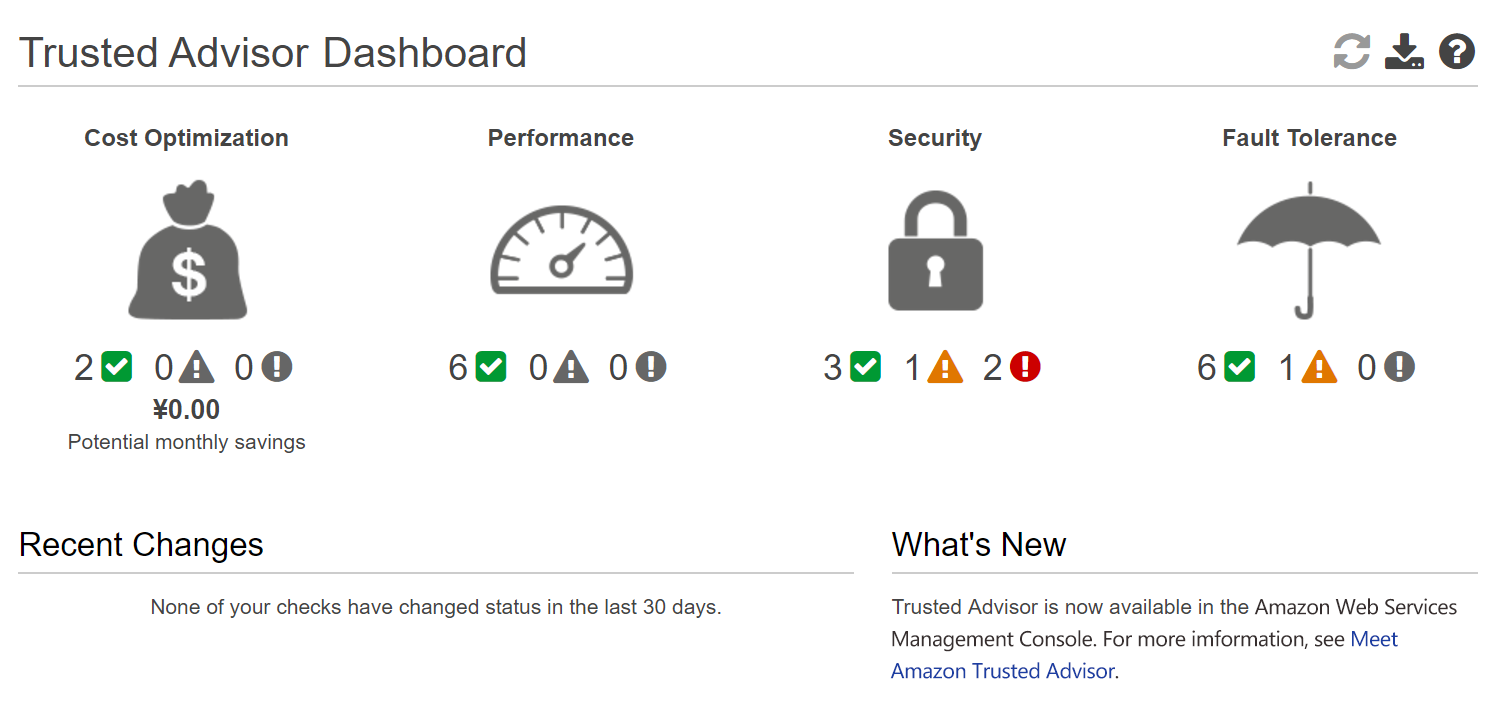
Cost Optimization
See how you can save money on Amazon Web Services by eliminating unused and idle resources or making commitments to reserved capacity.
Unassociated Elastic IP Addresses
Checks for Elastic IP addresses (EIPs) that are not associated with a running Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instance. EIPs are static IP addresses designed for dynamic cloud computing. Unlike traditional static IP addresses, EIPs can mask the failure of an instance or Availability Zone by remapping a public IP address to another instance in your account. A nominal charge is imposed for an EIP that is not associated with a running instance.
Security
Improve the security of your application by closing gaps, enabling various Amazon Web Services security features, and examining your permissions.
Security Groups - Specific Ports Unrestricted (Free!)
Checks security groups for rules that allow unrestricted access (0.0.0.0/0) to specific ports. Unrestricted access increases opportunities for malicious activity (hacking, denial-of-service attacks, loss of data). The ports with highest risk are flagged red, and those with less risk are flagged yellow. Ports flagged green are typically used by applications that require unrestricted access, such as HTTP and SMTP.If you have intentionally configured your security groups in this manner, we recommend using additional security measures to secure your infrastructure (such as IP tables).
Amazon S3 Bucket Permissions
Checks buckets in Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) that have open access permissions. Bucket permissions that grant List access to everyone can result in higher than expected charges if objects in the bucket are listed by unintended users at a high frequency. Bucket permissions that grant Upload/Delete access to everyone create potential security vulnerabilities by allowing anyone to add, modify, or remove items in a bucket. This check examines explicit bucket permissions, but it does not examine associated bucket policies that might override the bucket permissions.
Security Groups - Unrestricted Access
Checks security groups for rules that allow unrestricted access to a resource. Unrestricted access increases opportunities for malicious activity (hacking, denial-of-service attacks, loss of data).
Fault Tolerance
Increase the availability and redundancy of your Amazon Web Services application by take advantage of auto scaling, health checks, multi AZ, and backup capabilities.
Amazon EBS Snapshots
Checks the age of the snapshots for your Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) volumes (available or in-use). Even though Amazon EBS volumes are replicated, failures can occur. Snapshots are persisted to Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) for durable storage and point-in-time recovery.
Amazon EC2 Availability Zone Balance
Checks the distribution of Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances across Availability Zones in a region. Availability Zones are distinct locations that are designed to be insulated from failures in other Availability Zones and to provide inexpensive, low-latency network connectivity to other Availability Zones in the same region. By launching instances in multiple Availability Zones in the same region, you can help protect your applications from a single point of failure.
Load Balancer Optimization
Checks your load balancer configuration. To help increase the level of fault tolerance in Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) when using Elastic Load Balancing, we recommend running an equal number of instances across multiple Availability Zones in a region. A load balancer that is configured accrues charges, so this is a cost-optimization check as well.
Amazon S3 Bucket Logging
Checks the configuration of Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) buckets that have server access logging enabled. When logging is initially enabled, the configuration is automatically validated; however, future modifications can result in logging failures. This check examines explicit Amazon S3 bucket permissions, but it does not examine associated bucket policies that might override the bucket permissions.
Performance
Improve the performance of your service by checking your service limits, ensuring you take advantage of provisioned throughput, and monitoring for overutilized instances.
High Utilization Amazon EC2 Instances
Checks the Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances that were running at any time during the last 14 days and alerts you if the daily CPU utilization was more than 90% on 4 or more days. Consistent high utilization can indicate optimized, steady performance, but it can also indicate that an application does not have enough resources. To get daily CPU utilization data, download the report for this check.
Service Limits (Free!)
Checks for usage that is more than 80% of the service limit. Values are based on a snapshot, so your current usage might differ. Limit and usage data can take up to 24 hours to reflect any changes. In some cases, your usage might be greater than the indicated limit for a period of time.
Amazon EBS Provisioned IOPS (SSD) Volume Attachment Configuration
Checks for Provisioned IOPS volumes that are attached to an Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instance that is not Amazon EBS-optimized. Provisioned IOPS volumes in the Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) are designed to deliver the expected performance only when they are attached to an EBS-optimized instance.
Large Number of Rules in an EC2 Security Group
Checks each Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) security group for an excessive number of rules. If a security group has a large number of rules, performance can be degraded. For more information, see Amazon EC2 Security Groups.
Large Number of EC2 Security Group Rules Applied to an Instance
Checks for Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances that have a large number of security group rules. Performance can be degraded if an instance has a large number of rules.
Overutilized Amazon EBS Magnetic Volumes
Checks for Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) Magnetic volumes that are potentially overutilized and might benefit from a more efficient configuration. A Magnetic volume is designed for applications with moderate or bursty I/O requirements, and the IOPS rate is not guaranteed. It delivers approximately 100 IOPS on average, with a best-effort ability to burst to hundreds of IOPS. For consistently higher IOPS, you can switch to a General Purpose (SSD) volume or use a Provisioned IOPS (SSD) volume, which can deliver up to 4,000 IOPS. A Provisioned IOPS (SSD) volume is designed to deliver within 10% of the specified IOPS performance 99.9% of the time when it is attached to an Amazon EBS-optimized Amazon EC2 instance.